Saltwater vs Freshwater Aquarium: Pros, Cons & FAQs

Updated on

Choosing which aquarium type to purchase can be tricky. Both saltwater and freshwater tanks are desirable, each having its unique properties and aquatic inhabitant opportunities. With both so appealing, what are the differences between the two? In this article, we will explain the pros and cons of each aquarium and help you make an informed decision on which aquarium set-up is right for you.
The advantages and disadvantages of either a saltwater tank or a freshwater tank will give you the basis on which aquarium is right for you and meets your level of aquatic skills. The different aquarium environments allow you to keep different fish, invertebrates, and even plants! Use the article as guidance as to what your personal preference is.
Visual Differences
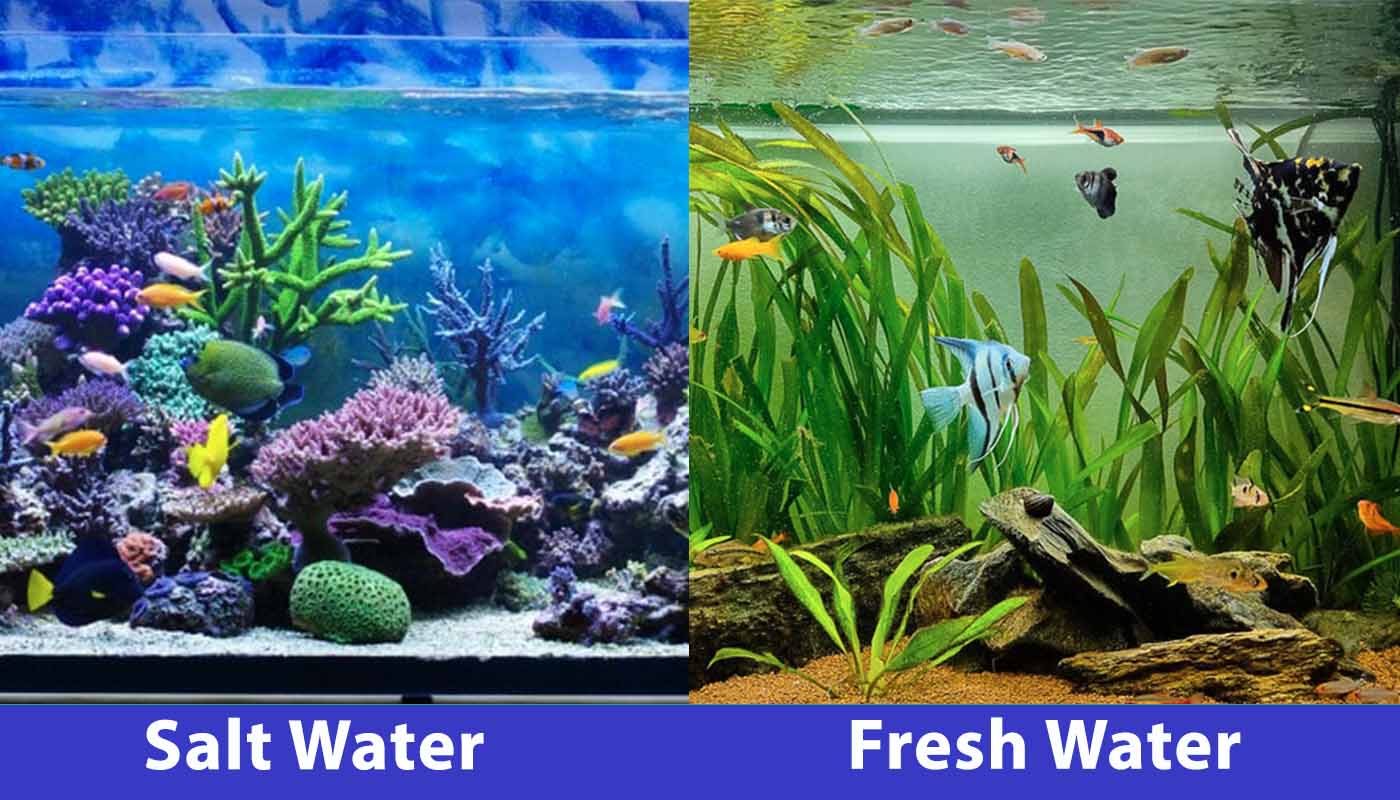

At a Glance
- Average size range: 20 to 150 gallons
- Additives: Aquarium salt and water conditioner
- Experience required: Knowledgeable/professional
- Average size range: 5 to 120 gallons
- Additives: Water conditioner
- Experience required: Beginner
Saltwater Aquarium Overview
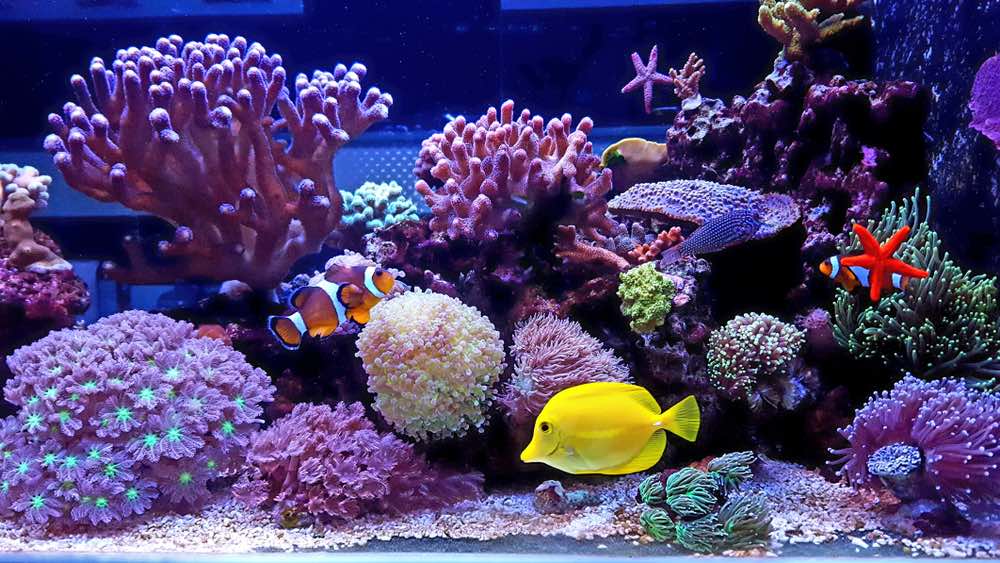

What is a Saltwater Aquarium?
A saltwater aquarium (aka a marine or reef aquarium) contains high amounts of pure sodium that is naturally dissolved into the water. This type of aquarium can house salt-tolerant species of fish, invertebrates, and plants that otherwise cannot survive in freshwater. Saltwater fish are generally not easy to come by and you may need to get your stock from a reputable breeder or large chain aquarium store. Saltwater tanks are more expensive to maintain and stock. Saltwater plants are generally hard to come by; therefore, many saltwater aquarists prefer to set up a reef tank.
The Ideal Temperature
Many saltwater fish are better suited to warmer water conditions. Although the temperature for a saltwater tank depends on the type of inhabitants you wish to keep, the general temperature is usually from 75–78 degrees Fahrenheit.
The pH for a Saltwater Aquarium
The alkalinity of the water is important for the health of your aquarium. Each species of saltwater fish or invertebrate requires a certain pH balance for healthy mucous production. An ideal range of 142–125ppm or 8–12dKH is recommended. You must regularly monitor the alkalinity in an aquarium, including the GH and KH (General Hardness, and Carbonate hardness). Marine fish require a high pH; the test results should be from 7.9 to 8.5.
Saltwater Aquarium Essential Equipment
Purchasing the necessary equipment for your tank is recommended before you start adding inhabitants. The standard equipment to maintain a saltwater aquarium may be pricey, but it is required.
- A large and spacious tank
- Aquarium salt and hydrometer
- A powerhead
- Live substrate and rock
- Heater
- Thermometer
- Air pump
- A large air stones
- Filtration equipment that can filter 5 times the water volume
- Test kit
- Tangs
- Anthias
- Angelfish (Dwarf or Large)
- Butterflies
- Clownfish
- Hamlets
- Hogfish
- Rabbitfish
- Sea horses
- Lobsters
- Marine crabs

Maintenance
The aquarium should be tested regularly to ensure there is enough salt content in the water. Diligent work should be done to ensure the aquarium is kept clean and controlled. Small changes such as a temperature or pH drop can harm sensitive marine fish. You will need to monitor the pH, KH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrates closely. One of the most important things to watch closely is the salinity of the aquarium, as marine fish need an appropriate salt content in the water to function properly.
Suitable for:
Saltwater aquariums are not suitable for novice aquarium owners. The knowledge and experience should be of a professional level. Taking on a saltwater aquarium is a lot of work, something novice aquarists are not yet familiar with. You need to be able to provide the right treatment and be able to house and care for the inhabitants more than freshwater fish.
Marine fish are very sensitive and cannot tolerate most beginner mistakes. A saltwater aquarium is best suited for an experienced aquarist who has done extensive research on saltwater aquariums and has the time and effort to appropriately care for one. You will need to have a pet store close by that sells marine-based fish products, as they are hard to come by.
- Wide variety of colorful marine fish to choose from
- The challenge and opportunities that are opened up
- Provides a new experience for the standard hobbyist
- Expensive
- Marine fish are sensitive to sudden environmental changes
- Not suitable for beginner aquarists
Freshwater Aquarium Overview
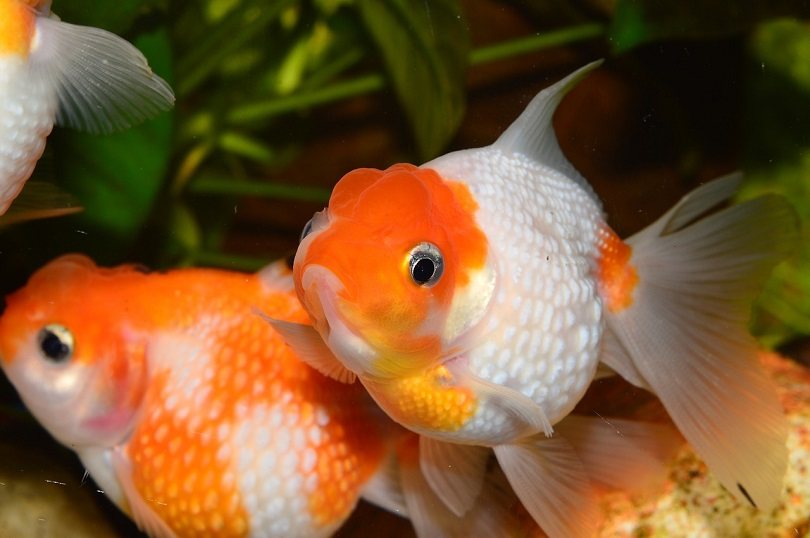

What is a Freshwater Aquarium?
Freshwater aquariums use the standard low salinity water that is rich in ions and minerals. It is one of the most popular types of aquariums to keep. The water only needs to be treated with a quality de-chlorinator; no added salts are required. A freshwater tank can house a wide variety of inhabitants and plants. These are some of the easier aquariums to keep, with the fish being less sensitive than marine fish. These aquariums are less expensive and more affordable to the average hobbyist.
The Ideal Temperature
Freshwater aquariums are categorized into cold-water aquariums, where the ideal temperature is between 68-77 degrees Fahrenheit, and tropical aquariums. A tropical freshwater aquarium requires a heater and a temperature range between 74-86 degrees Fahrenheit.
The pH for a Freshwater Aquarium
Depending on the type of aquatic inhabitant and plants you want to house in the aquarium, you will need a pH balance from 6.0 to 7.8. Freshwater fish can tolerate small fluctuations in pH. It is important to keep an eye on the KH and GH. Some freshwater fish prefer more acidic water whereas some prefer water with a high alkaline balance.
Freshwater Aquarium Essential Equipment
Freshwater aquariums require less equipment than a saltwater tank. The benefit is that some inhabitants do not require a fully kitted aquarium. Betta fish are an example of fish that prefer a smaller environment with a low-flow filter and air stone.
- Goldfish
- Koi
- Betta/Siamese fighter fish
- Guppies
- Mollies
- Swordtails
- Tetras
- Danios
- African Cichlid
- Corydoras
- Rasboras
- Shrimp
- Apple snails

Maintenance
Freshwater aquariums are generally low maintenance. Cycling the aquarium is simple and there are many products on the market for freshwater aquariums. Regular water testing for ammonia, nitrite, and nitrates should be conducted. A thermometer should be placed in the aquarium to monitor the temperature; most freshwater fish can handle a mild fluctuation in temperature, but this is not ideal. Gravel vacuuming can be done at least three times a month depending on how big and stocked your aquarium is. Most freshwater fish prefer a lot of decoration in the aquarium for safety.
Suitable for:
Freshwater aquariums are well suited for novice and seasoned aquarists alike. The maintenance is simple, and the inhabitants are hardy. This makes them able to withstand some common beginner mistakes. However, thorough research is vital before you set up and purchase inhabitants for your aquarium. Most pet stores stock a variety of freshwater products.
- Low maintenance
- Inexpensive
- Suitable for beginner aquarists
- Frequent water testing should be conducted
- Freshwater fish are prone to a variety of diseases
Additional Information
The Main Differences Between Saltwater and Freshwater Aquariums
A tabulated short version of the main differences between these two types of aquariums.
| Saltwater Aquarium: | Freshwater Aquarium: |
| Requires aquarium salt and de-chlorinator | Only requires de-chlorinator |
| Aquaria need to be reefed | Plastic decorations can be used |
| Expensive equipment and maintenance | Generally inexpensive depending on inhabitants |
| An interesting variety of inhabitants | Cold and tropical water inhabitants |
Why Choose a Saltwater Aquarium?
Saltwater aquariums offer a different experience in the aquarium industry. The saltwater hobby is generally something seasoned aquarists see as a welcomed challenge and professional experience. Saltwater tanks are commonly kept to preserve some species of marine inhabitants. Owning a saltwater aquarium gives the aquarists a sense of pride, as maintaining a saltwater aquarium is hard work! A great reward is to see a flourishing saltwater aquarium fully reefed.
Why Choose a Freshwater Aquarium?
Freshwater aquariums provide an opportunity to house different inhabitants in a variety of setups and environments. Freshwater aquariums are suited for aquarists who do not have a lot of time in the day to maintain a tank. Keeping a freshwater aquarium provides the visual aspect an aquarium brings to an environment with a bonus of low maintenance.
The Different Size of Inhabitants
Marine fish are generally larger than freshwater species of fish. Therefore, marine fish require larger aquariums to be healthy and thrive. If you are looking for brightly colored and large inhabitants, a saltwater aquarium is your best choice.
The Amount of Equipment Used in a Saltwater and Freshwater Aquarium
Freshwater aquariums require less equipment than saltwater aquariums do. Freshwater tanks require a heater if the aquarium is for tropical fish species. The equipment is cheaper and more available than saltwater equipment.
Saltwater aquariums require a hefty amount of equipment to ensure the balance and ecosystem mimics a marine fish’s natural habitat as closely as possible.
Placement
Small freshwater aquariums can be situated on desks and small spaces depending on the size. Small 2.5 to 10-gallon tanks can be comfortably fitted in a bedroom or office. Saltwater tanks are larger and should be placed in an area that receives moderate lighting for at least 6 hours. The overall size makes them less suitable to be placed on a small office desk.
Which Aquarium Setup is Right for You?
If you are prepared to dive into the upkeep and opportunities a saltwater aquarium can provide, while having extensive knowledge of the care of marine fish and their environment, a saltwater aquarium may be just right for you!
If you are a novice aquarist searching for the perfect aquarium type to start with, a freshwater aquarium is a good choice. If you manage a busy lifestyle alongside being part of the aquarium hobby, freshwater aquariums provide you with the opportunity to enjoy the hobby while having beautiful inhabitants and decoration options to choose from.
We hope this article has outlined the basis of both freshwater and saltwater tanks and provided you with the necessary information to persuade you to purchase an ideal aquarium.
Featured Image Credit: Jumpstory